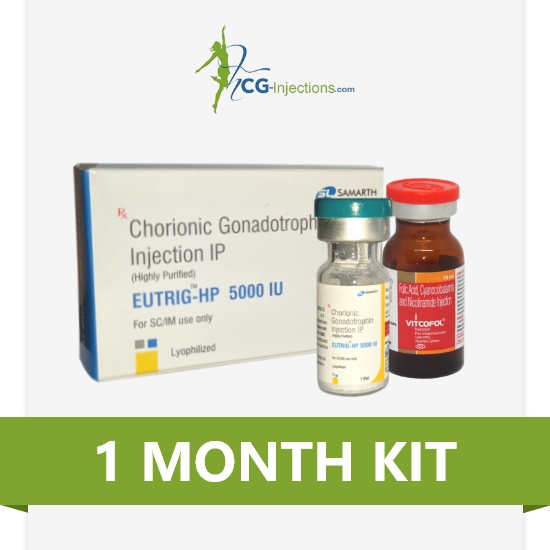
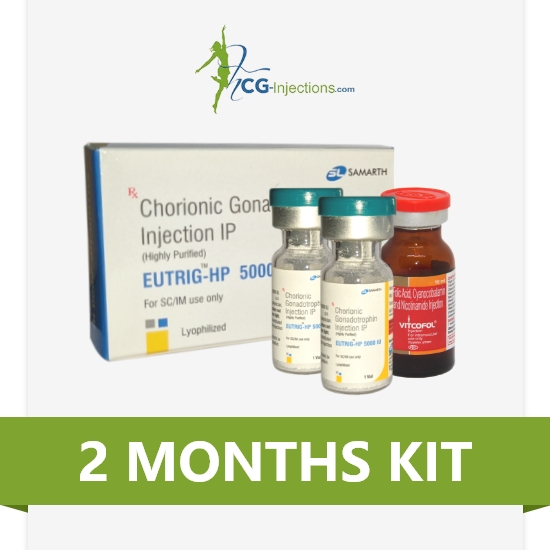
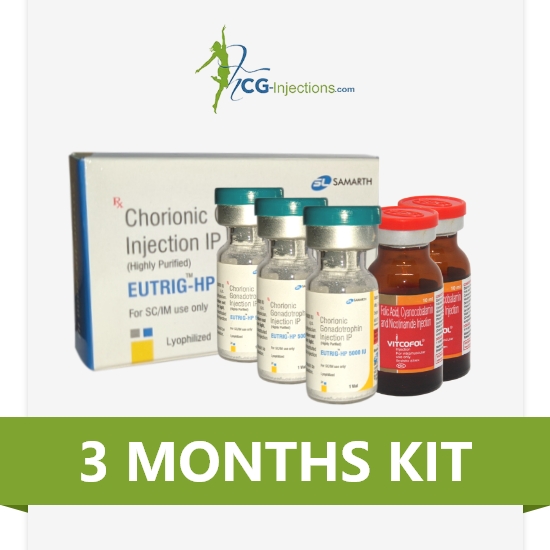
SELECT YOUR WEIGHT LOSS GOAL
Why should I Buy From hCG Injections Shop?
See what our
SATISFIED CUSTOMERS
are saying about our hCG Kits.
20% discount to all our hcg diet customers who are willing to share their stories with before and after pic to encourage other people to give this a try, go ahead look and see what our customers shared with us; after all the best arguments results is results!
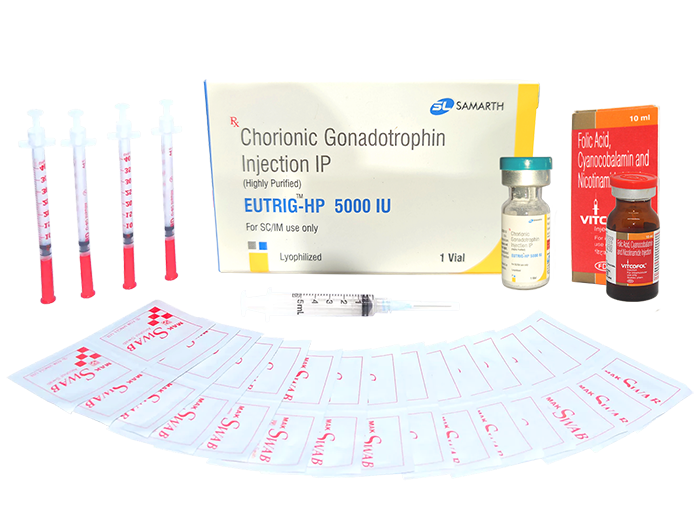
hCG Injections Shop sells pharma grade freeze dry hCG
This is not homeopathic “natural/herbal mix” This is pure and real Pharma Grade products you can find in a hospital or at the local clinic.
When you buy from us, you buy the best there is available online.
Buying From hCG Injections Shop?
HCG Injections Shop only offer Pharmaceutical Grade Products. To prove this we have provided a Certificate of Analysis in our product section that this is the purest and real hormone you can get can overseas at the lowest possible price.
What Do We Offer?
We not only offer all that you may need to begin but we also offer support and help for our ongoing hCG Kits users, this means we will give you some tips and advise as best we can – we even provide access toartciles and blogs post and anything else you might need to be on your way to a fitter and slimmer body !
HCG Diet Tips
HCG Diet Holiday Tips
HCG Diet for Men
How to Avoid Food Temptations after the HCG Diet

HCG Friendly Recipes
We are gathering all the best and healthies recipes for your hCG diet – all the best food to complement your hCG protocol so you can shed those pounds away!